When it comes to a multi-tier router architecture you will be connecting Tier-1 router(s) to an existing Tier-0 router. East-West routing is performed by the DR (distributed Router) in the Tier-1 router. The Tier-0 provides services and external connectivity.
Some things to be aware of:
- When the service and distributed routers are created, they are interconnected through the router-link port between them.
- Each tier-0-to-tier-1 peer connection is provided a /31 subnet within the 100.64.0.0/10 reserved address space (RFC6598).
- When a Tier-1 Gateway is connected to Tier-0 Gateway the management plane configures a default route on T1 with next hop IP address as Routerlink IP of T0 (100.64.128.0/31)
- To provide reachability to subnets connected to the T1 Gateway the Management Plane configures static routes on the T0 Gateway for all the LIFs connected to T1 with a next hop IP address as T1 Routerlink IP (100.64.128.1)
A tiered architecture has the following features and functions:
- Supports tenant isolation
- Includes separate controls for different admin domains
- Eliminated physical dependency when new tenants are introduced.
Step 1. Edit your existing T1 Router
Networking>Tier-1 Gateway
—Edit existing T1
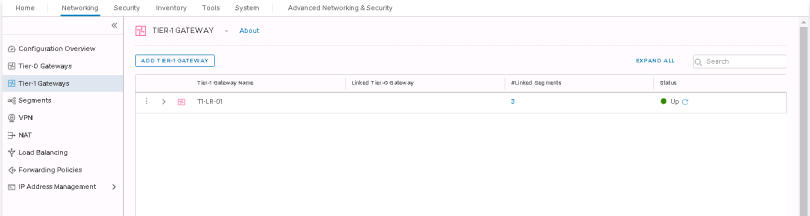
Step 2. Click the drop down under Linked Tier-0 Gateway & select your existing T0 router.

Save>close editing

Step 3. Verify connectivity by performing ping tests
Summary
As you can see above the 3 segments tied to our T1 is now seen as linked allowing them access beyond their own T1. Linking a T1 to a T2 is a simple process and isn’t very complicated. I hope this article helps simplify the process.
